
Hypothesis - Floride added to a toothpaste protects teeth against cavities. Null Hypothesis - Water added to a toothpaste has no effect against cavities. Hypothesis - Water added to a toothpaste protects teeth against cavities. Consider the following examples: Example 1
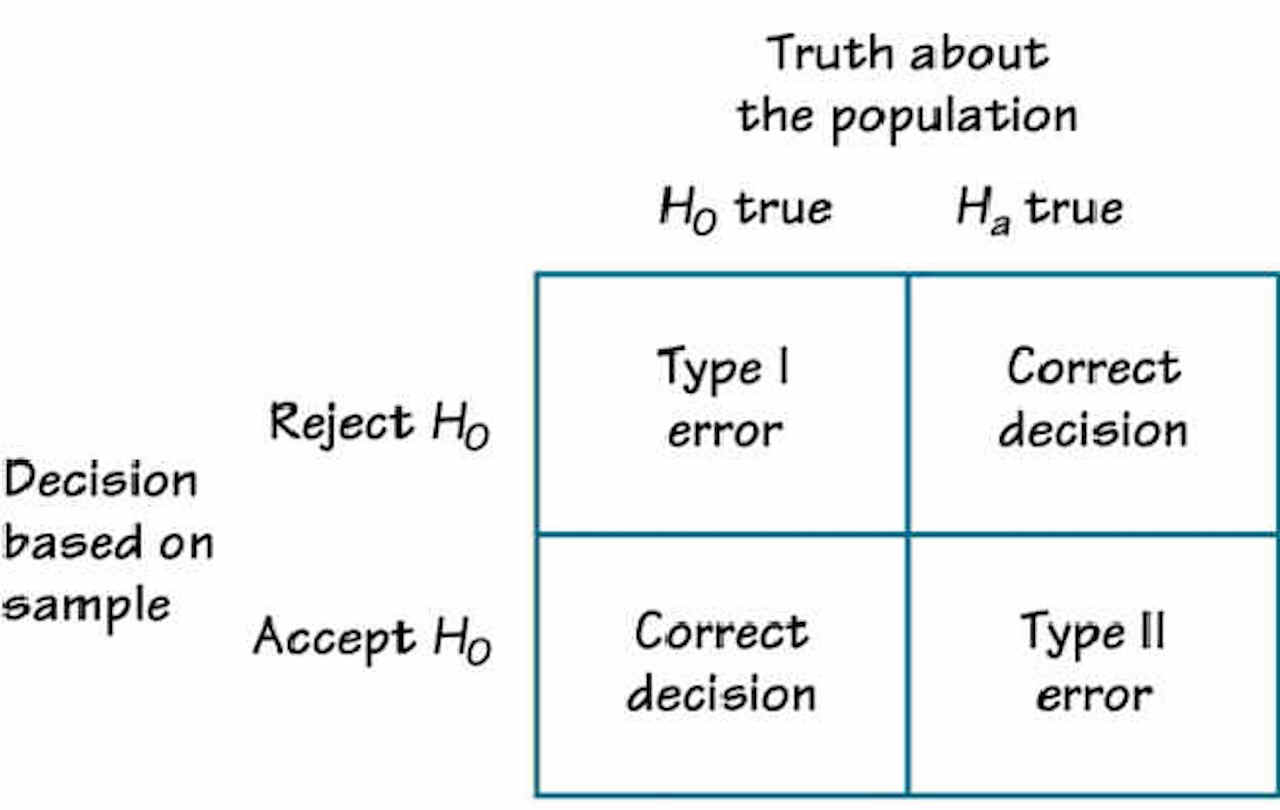
Null Hypothesis refers to a statement which nullifies the contrary with evidence. Type I error represents the incorrect rejection of a valid null hypothesis whereas Type II error represents the incorrect retention of an invalid null hypothesis. Type I and Type II errors signifies the erroneous outcomes of statistical hypothesis tests. Regression Intercept Confidence Interval.Process Capability (Cp) & Process Performance (Pp).



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
